American Panorama: Part II
This is the second half of a review of American Panorama (you can read Part I here). Together, the two posts are a follow-up to my earlier call for digital historians to more actively engage with the historical contributions of each other’s projects.
Part II. The Overland Trails, 1840-1860
Between 1840 and 1860 several hundred thousand people traveled westward across the United States, most of them ending up in California, Oregon, and Utah. Their migration has become a foundational element of American history, conjuring up visions of covered wagons and hardy pioneers. Or, if you grew up playing the educational computer game The Oregon Trail: floppy disks, pixelated oxen, and exciting new words like “dysentery.” The topic has been exhaustively studied by genealogists, historians, and millions of schoolchildren over the years. American Panorama attempts to break new ground on what is, like the trail itself, well-trodden soil.
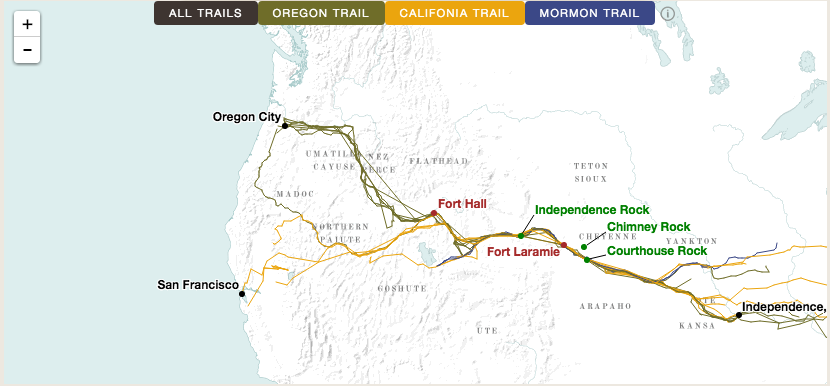
The Overland Trails follows a similar visual layout as The Forced Migration of Enslaved People, with multiple panes showing a map, a timeline, aggregated data, and the expandable text from twenty-two trail diaries. Far more so than The Forced Migration of Enslaved People, however, it puts these written narratives into the spotlight. The visualization includes the full text of each diary rather than brief excerpts. Clicking on a specific diarist allows you to read all of their entries, with a linked footnote to the original source. As you scroll through the entries, clusters of dots track the progress of the emigrant’s journey on the map as they pass between landmarks like Courthouse Rock or Fort Laramie.
Two other panes provide context for that particular year: a short summary of trail activity and a small map breaking down the estimated annual migration to California, Oregon, and Utah. The timeline uses small multiples for each year that plot the seasonal progression of emigrant journeys on its x-axis and, somewhat confusingly, the (horizontal) longitude coordinates of these journeys on its vertical axis. Timeline aside, the overall reading experience is both intuitive and seamless. More importantly, the visualization strikes a balance between detail and context, weaving the full text of individual sources within a larger spatial and historical tapestry. In many ways, this is digital design at its best. But why does this elegant design matter? What is the historical payoff? The Overland Trails makes two contributions to the topic of westward migration - one archival and the other interpretive.
First, The Overland Trails gives us not just a new, but a better platform for reading and understanding the topic’s source base. The trail diary was a genre unto itself during the mid-nineteenth century. They were often written to serve as a kind of guide to help family or friends follow them westward, recording daily mileage, landmarks, trail quality, and the availability of water and grass. These details made the diaries immensely helpful for future emigrants, but immensely boring for future historians. Take an entry written by James Bennett on July 12th, 1850:
Friday 12th-After ten miles travel this day over a heavy, sandy and barren road, we reached Sweet Water river, where we took dinner. Here we found the grass very short and as our cattle were nearly exhausted by hard work and scant feed, we drove off the road five miles to the right, where we found excellent grass and a good spring.
Now imagine reading thousands of entries exactly like this one. You start to get hungry for anything that breaks the monotony of the trail: white-knuckled river crossings, exchanges with passing Indians, or fiery arguments about whether or not to travel on the Sabbath. Moreover, as a reader we often don’t care all that much about where these juicy episodes took place - does it really matter if they occurred in western Nebraska, northern Utah, or eastern Oregon? The nebulous space of “The Trail Experience” serves as a stand-in for specific geography of where things happened. But the loss of geographic context risks distorting the lived reality of nineteenth-century emigrants. For them, trail life was overwhelmingly defined by geography: boring, repetitive, grinding travel along an established trail itinerary, with mileage tallies or landmark notations acting as a means of marking their progress through that geography. American Panorama captures the experience of overland travel far more effectively than simply reading trail diaries on their own. As simple as it sounds, linking individual entries to their location on a map illustrates the small-scale, incremental geography that made up this massive, large-scale migration.
The second historical contribution of The Overland Trails involves a broader spatial reinterpretation of westward expansion. The phrase itself - “western expansion” conjures up the image of a wave of Anglo-American settlers washing over the continent. This was the geography embedded in Manifest Destiny iconography and Frederick Jackson Turner’s famous frontier thesis.
 Source: Wikimedia Commons
Source: Wikimedia Commons
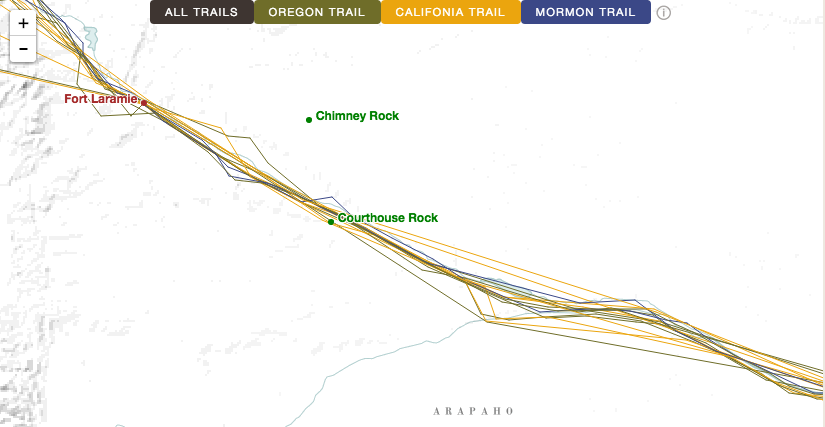
American Panorama presents a much different geography. Western migration was not a wave; it was a narrow river. Hundreds of thousands of people may have traveled across the western interior between the 1840 and 1860, but they did so along a severely restricted corridor of travel. This might seem obvious; the Overland Trail was, after all, a trail. But the trail’s meaning has come to embody a certain idea of mobility, not just in terms of traveling westward to Oregon or California, but of experiencing and claiming the vast swath of land that lay in between. When mapped, however, the journeys of twenty-two emigrants resemble tightly braided cords that only gradually fray as they approach the Pacific Coast. Overland travelers operated in a tightly constrained space.
To take one example: although emigrants technically traversed from one side of Nebraska Territory to the other, most travelers didn’t see very much of it. The grinding necessity of daily travel kept them pinned along the Platte River. American Panorama illustrates just how narrow this pathway was and how infrequently emigrants deviated from it.
In the mid-nineteenth century, the interior of the western United States was seen as a region to pass through as quickly as possible, an area that had long been labeled “The Great American Desert,” or in historian Elliott West’s words, “a threatening void.” (The Contested Plains, 122) Much of the western interior was made up of territory that was ostensibly claimed by the United States but that remained largely ungoverned and unsettled by Anglo-Americans. American Panorama effectively recreates this geography through visual design: bright, sharp lines track the emigrants’ journeys along the trail, interspersed with landmarks and forts shown in equally bright colors. This tightly demarcated trail geography pops out from the map as it snakes across a minimalist base layer entirely devoid of the familiar political boundaries of states or territories. Instead, the underlying map consists of terrain, sparse water features, and the locations of Indian groups such as the Cheyenne in the central plains or the Goshute near Great Salt Lake. The Overland Trails manages to capture the experience of traversing a semi-arid, mountainous region still occupied by native people, one that was seen as largely off-limits for Anglo-American settlement.
The project’s cartographic achievement comes with a cost, however. The presence of native groups played a crucial role in shaping mid-century views of the interior. As historian Susan Schulten notes, “erasing Native Americans from both mental and actual maps” (29) was a central process in the eventual shift from seeing the western interior as an inviting area to settle rather than a forbidding area to traverse. To their credit, the designers of The Overland Trails put native people back on the map. The problem comes from the way in which they do so. The mapmakers label Indian groups using a muted gray color that is nearly identical to the map’s base terrain. Moreover, changing the zoom level causes some labels to shift locations or disappear entirely in order to avoid overlapping with the trail and its landmarks. The overall effect is to weave native groups into the natural landscape, making them visually analogous to the map’s rivers or mountains. This cartographic design ends up conflating native people and the environment - a deeply problematic notion that remains stubbornly lodged in the popular imagination. The visualization builds a marvelous stage for overland emigrants, but its set design turns Indians into a backdrop.
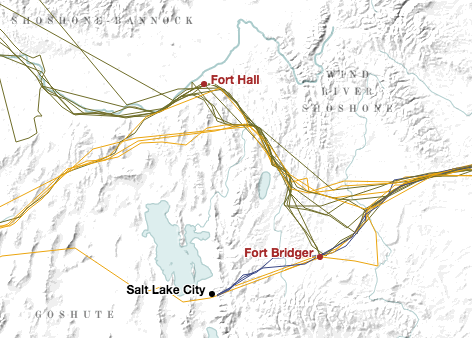
I don’t mean to quibble over (literal) shades of gray. After all, the map’s creators made a concerted effort to include Indian groups - the same can’t be said of other many other historical projects, digital or otherwise. But the project’s cartography highlights a common tension between digital design and historiography. From a design standpoint, the creators of The Overland Trails make all the right decisions. Brightly colored overland routes are foregrounded against a muted base map, including unobtrusive gray labels of Indian groups that give readers contextual information while keeping their attention firmly focused on the emigrant journeys themselves. When those same labels disappear or change locations depending on the zoom level, it helps avoid visual clutter. The problem is that effective digital design can run headlong into fraught historiographical issues, including the contentious idea of the “ecological Indian” and a longstanding cartographic tradition of using maps to marginalize and erase native claims to territory in the West.
Visual design is not the only sticking point for The Overland Trails and its place within western historiography. The visualization is, at its core, a digital archive of primary sources. As I’ve already noted, its interface contributes a new and fascinating way of reading and understanding these sources. What troubles me is the privileging of this particular archive. To be blunt: do we really need a new way of reading and understanding the experience of mostly white, mostly male pioneers whose stories already occupy such a central place in American mythology?
The historical commemoration of overland emigrants began almost as soon as their wagons reached the Pacific Coast. Western pioneer associations held annual conventions and published nostalgic reminiscences that romanticized their journeys. Historians, meanwhile, largely followed the blueprint of Frederick Jackson Turner, who immortalized the march of pioneer-farmers carrying the mantle of civilization westward. Nearly a century passed before historians began to reassess this framework, from uncovering the ways that gender shaped life on the trail to, more recently, interpreting overland migration as a “sonic conquest.” (to use Sarah Keyes’s formulation).
More often than not, however, historical treatments of the Overland Trail still tend to resemble book titles like Wagons West: The Epic Story of America’s Overland Trails, or quotes like, “An army of nearly half a million ragged, sunburned civilians marched up the Platte in the vanguard of empire…they emerge from their collective obscurity to illuminate a heroic age in American history.” (Merrill Mattes, Platte River Road Narratives, xiv) The Overland Trails doesn’t explicitly advance this viewpoint, but nor does it move away from it in any substantive way. The informational text accompanying the visualization’s timeline can, at times, read like a “greatest hits” of western lore: the Donner Party, the Gold Rush, Indian fighting, and the Pony Express (its freshest material centers on Mormon migration). The visualization’s space constraints leave precious little room for important historical nuance, leading to generalizations such as “White settlement in the West was disastrous for Indians everywhere.”
To reiterate a point I made in the first part of my review of American Panorama: prioritizing user exploration over authorial interpretation comes with risks. I don’t want to minimize the significance of The Overland Trails, because it contributes a truly valuable new interface for conceptualizing nineteenth-century historical geography and the experience of overland travel. But the project uses a novel framework to deliver largely tired content. My guess is that its selection of content was based on the fact that these particular diaries were already digitized. This kind of pragmatism is a necessary part of digital history. But explaining the interpretive implications of these decisions, not just the nitty-gritty methodological details, often requires a more robust and explicit authorial voice than many digital history projects seem willing to provide.
My hope is that The Overland Trails will serve as a prototype for visualizing other movement-driven sources. To that end, American Panorama has given outside researchers the ability to build on this framework by making the project’s source code available on Github. The Github repository highlights the open-ended nature of the project, as its creators continue to improve its visualizations. In a similar vein, American Panorama’s team has several new visualizations to come that examine redlining, urban renewal, and presidential voting. I have high expectations, and I hope that other historians will join me in giving them the substantive engagement they deserve.